Agents record when a protection module rule or condition is triggered (this is known
as a security event). Agents and Server & Workload Protection also records when administrative or system-related events occur (this is known as
a system event), such as an administrator logging in, or agent software being upgraded.
Event data is used to populate the various reports and graphs in Server & Workload Protection.
To view events, go to Events & Reports in Server & Workload Protection.
Location of event logs on the agent
Location varies by the computer's operating system. On Windows, event logs are stored
in the following location:
C:\Program Data\Trend Micro\Deep Security Agent\DiagOn Linux, event logs are stored in the following location:
/var/opt/ds_agent/diagThese locations only contain standard-level logs; diagnostic debug-level logs have
a different location. For performance reasons, debug-level logging is not enabled
by default. You should only enable debug logging if diagnosing an issue with Trend
Micro technical support, and make sure to disable debug logging when you are done.
For more information, see Enabling detailed logging on Deep Security Agent (DSA).
Timing of event forwarding
Most events that take place on a computer are sent to Server & Workload Protection during the next heartbeat operation except the following, which is sent right away
if communication settings allow relays or agents to initiate communication:
- Smart Scan Server is offline
- Smart Scan Server is back online
- Integrity Monitoring scan is complete
- Integrity Monitoring baseline created
- Unrecognized elements in an Integrity Monitoring Rule
- Elements of an Integrity Monitoring Rule are unsupported on the local platform
- Abnormal restart detected
- Low disk space warning
- Log Inspection offline
- Log Inspection back online
- Reconnaissance scan detected (if the setting is enabled in
Events retention periods
Server & Workload Protection retains security events for four weeks and system events for thirteen weeks. If you
require a longer event retention period, consider exporting events to an external
SIEM. For more information, see Forward Server & Workload Protection events to an external syslog or SIEM server.
Event history is retained for the following events:
- Anti-Malware events
- Application Control events
- Firewall events
- Integrity Monitoring events
- Intrusion Prevention events
- Log Inspection events
- Web Reputation events
- System events
- Device Control events
System events
All the Server & Workload Protection system events are listed and can be configured on the tab. You can set whether to record the individual events and whether to forward them
to a SIEM system. For details on system events, see System events.
Security events
Each protection module generates events when rules are triggered or other configuration
conditions are met. Some of this security event generation is configurable. For information
on specific types of security events, see the following:
- Anti-Malware events
- Identified files
- Application Control events
- Firewall events
- Integrity Monitoring events
- Intrusion Prevention events
- Log Inspection events
- Web Reputation events
- Device Control events
The firewall stateful configuration in effect on a computer can be modified to enable
or disable TCP, UDP, and ICMP event logging. To edit the properties of a stateful
firewall configuration, go to . The logging options are in the TCP, UDP, and ICMP tabs of the firewall stateful configuration's Properties window. For more information about firewall events, see Firewall events.
View events associated with a policy or computer
Both the Policy editor and the Computer editor have Events tabs for each protection module. The Policy editor displays events associated with
the current policy. The Computer editor displays events specific to the current computer.
View details about an event
To view details about an event, double-click it.
The General tab displays the following:
- Time: The time according to the system clock on the computer hosting Server & Workload Protection.
- Level: The severity level of event that occurred. Event levels include Info, Warning, and Error.
- Event ID: The event type's unique identifier.
- Event: The name of the event (associated with the event ID).
- Target: The system object associated with the event will be identified here. Clicking the object's identification displays the object's properties.
- Event Origin: The Server & Workload Protection component from which the event originated.
- Action Performed By: If the event was initiated by a user, that user's username will be displayed here. Clicking the username will display the User Properties window.
- Manager: The hostname of the Server & Workload Protection computer.
- Description: If appropriate, the specific details of what action was performed to trigger this event are displayed here.
The Tags tab displays tags that have been attached to this event. For more information on
event tagging, see , and Apply tags to identify and group events.
Filter the list to search for an event
The Period toolbar lets you filter the list to display only those events that occurred within
a specific time frame.
The Computers toolbar lets you organize the display of event log entries by computer groups or
computer policies.
Clicking toggles the display of the advanced search bar.
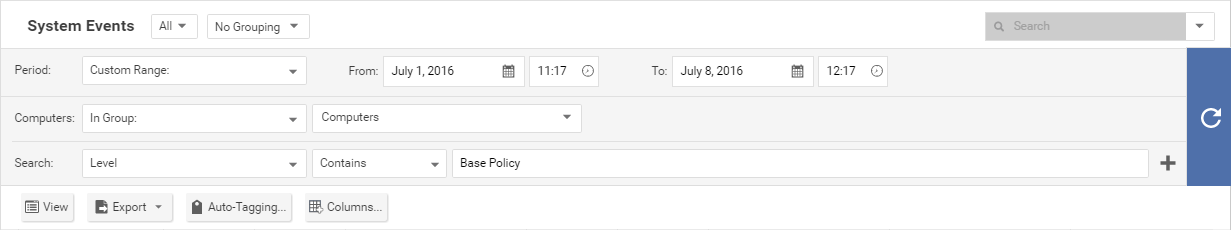
Clicking Add Search Bar (+) to the right of the search bar displays an additional search bar, which allows
you to apply multiple parameters to your search. When you are ready, click Submit Request (right arrow) located on the right.
Export events
You can export displayed events to a CSV file (paging is ignored, all pages are exported).
You have the option of exporting the displayed list or the selected items.
Improve logging performance
You can do the following to improve the performance of event collection:
- Reduce or disable log collection for computers that are not of interest.
- Consider reducing the logging of firewall rule activity by disabling some logging options in the firewall stateful configuration Properties. For example, disabling the UDP logging eliminates the Unsolicited UDP log entries.


