Use the Command Line Interface (CLI) to deploy a Service Gateway virtual appliance with Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM).
Verify that system requirements are met. For more information, see Service Gateway appliance system
requirements.
NoteThe following KVM instructions and screen captures were valid as of September 22,
2025. For further help, check your KVM documentation.
|
Procedure
- Go to .
- Click Download Virtual Appliance.The Service Gateway Virtual Appliance panel appears.
- Select KVM (QCOW2).
- Click Download Disk Image to download a QCOW2 file.

Tip
Copy the registration token for later steps. The registration token will expire within 24 hours if not used. - Upload the disk image to the Linux machine.
- Verify that the KVM virtualization environment is ready on the Linux host by running
the following commands:
-
sudo systemctl status libvirtd.socketSample output:systemctl status libvirtd.socket # ● libvirtd.socket - libvirt legacy monolithic daemon socket # Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/libvirtd.socket; enabled; preset: disabled) # Active: active (running) since Fri 2025-08-01 23:35:42 CST; 1 week 2 days ago # Until: Fri 2025-08-01 23:35:42 CST; 1 week 2 days ago # Triggers: ● libvirtd.service # Listen: /run/libvirt/libvirt-sock (Stream) # CGroup: /system.slice/libvirtd.socket # # Aug 01 23:35:42 Rocky-Linux systemd[1]: Listening on libvirt legacy monolithic daemon socket.
-
sudo kvm-ok(if supported on your machine)Sample output:sudo kvm-ok # INFO: /dev/kvm exists # KVM acceleration can be used
-
- Upload the image to the Linux machine, for example, upload it to
/kvm. The full path is/kvm/sg-va-3.0.23.10xxx.qcow2.
- Verify that the KVM virtualization environment is ready on the Linux host by running
the following commands:
- Create a virtual machine by using either command-line tools or GUI.
-
Use the command-line tool virt-install to create a virtual machine.
-
Specify the following settings in the command:
-
name: Specify the VM name, e.g., sg-va -
vcpu: Specify the desired configuration, e.g., 8 -
memory: Specify the desired configuration, e.g., 12 GB -
disk: Assign the Service Gateway image path as the system disk -
network: Configure the network interface -
graphics: Enable VNC access to the VM viavnc://{host-machine}:5911after deployment -
osinfo: Userhel7.0as the OS variant
Below is an example of the complete command:virt-install \ --name sg-va \ --cpu host-passthrough,cache.mode=passthrough \ --vcpu 8 \ --memory 12288 \ --disk /kvm/sg-va-3.0.23.10xxx.qcow2,bus=virtio \ --network network=hostbridge,model=virtio \ --graphics vnc,port=5911,listen=0.0.0.0 \ --video vga \ --osinfo rhel7.0 \ --noautoconsole \ --import # Starting install... # Creating domain... | 0 B 00:00:00 # Domain creation completed.
-
-
After creating the virtual machine, use the
virshcommand to check its status. You should be able to see the VM is running.virsh list # Id Name State # ---------------------- # 2 sg-va running
-
-
As an alternative, if you have KVM management tools installed on the host machine, you can use those tools to deploy and manage the VM.
Virtual Machine Manageris used as an example in the following steps:-
Launch Virtual Machine Manager.
-
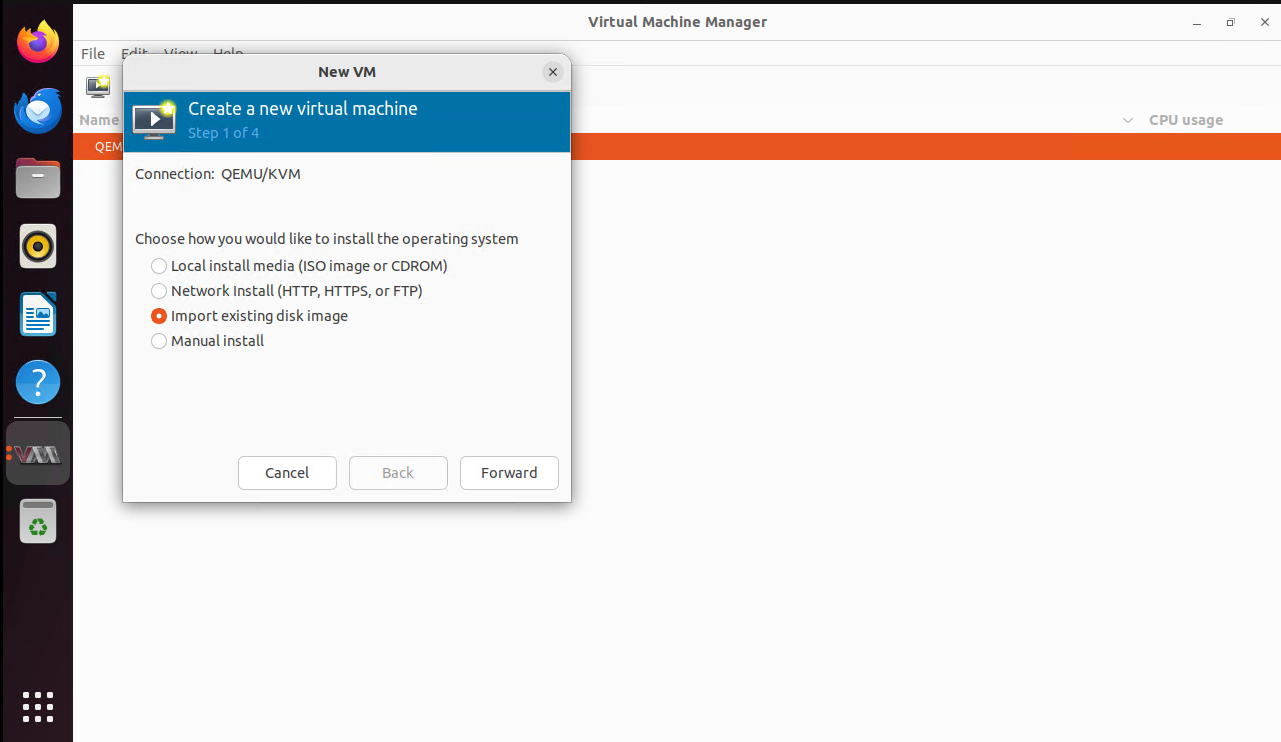
Import the existing disk image to create the VM.
-
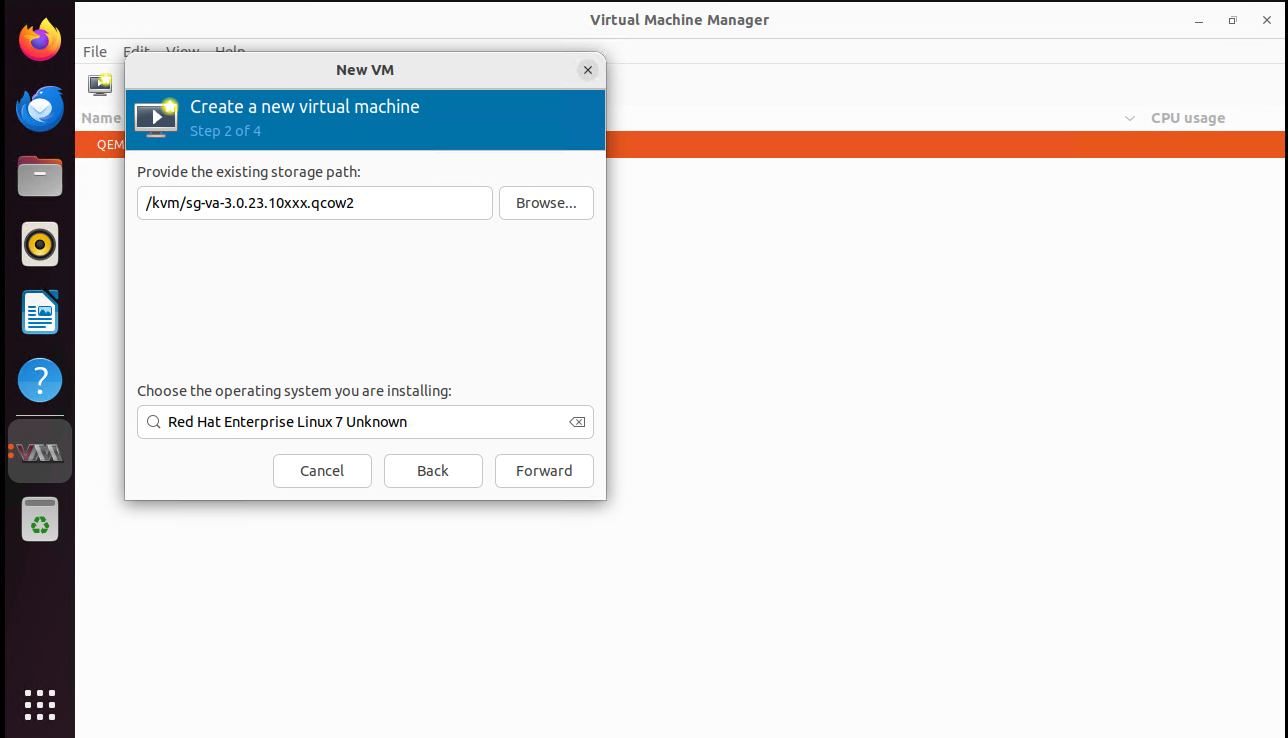
Specify the image path and the operating system you are installing.
-
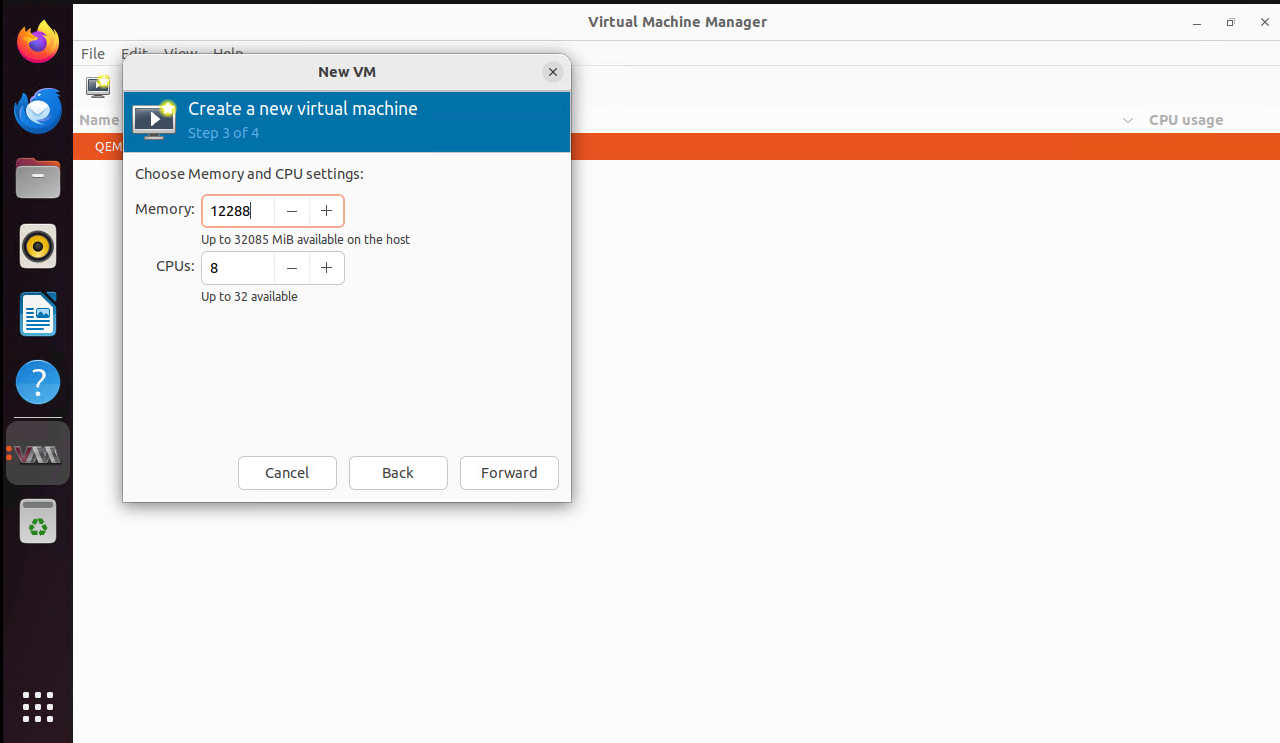
Assign CPU and memory resources.
-
Specify the VM name and network configuration.
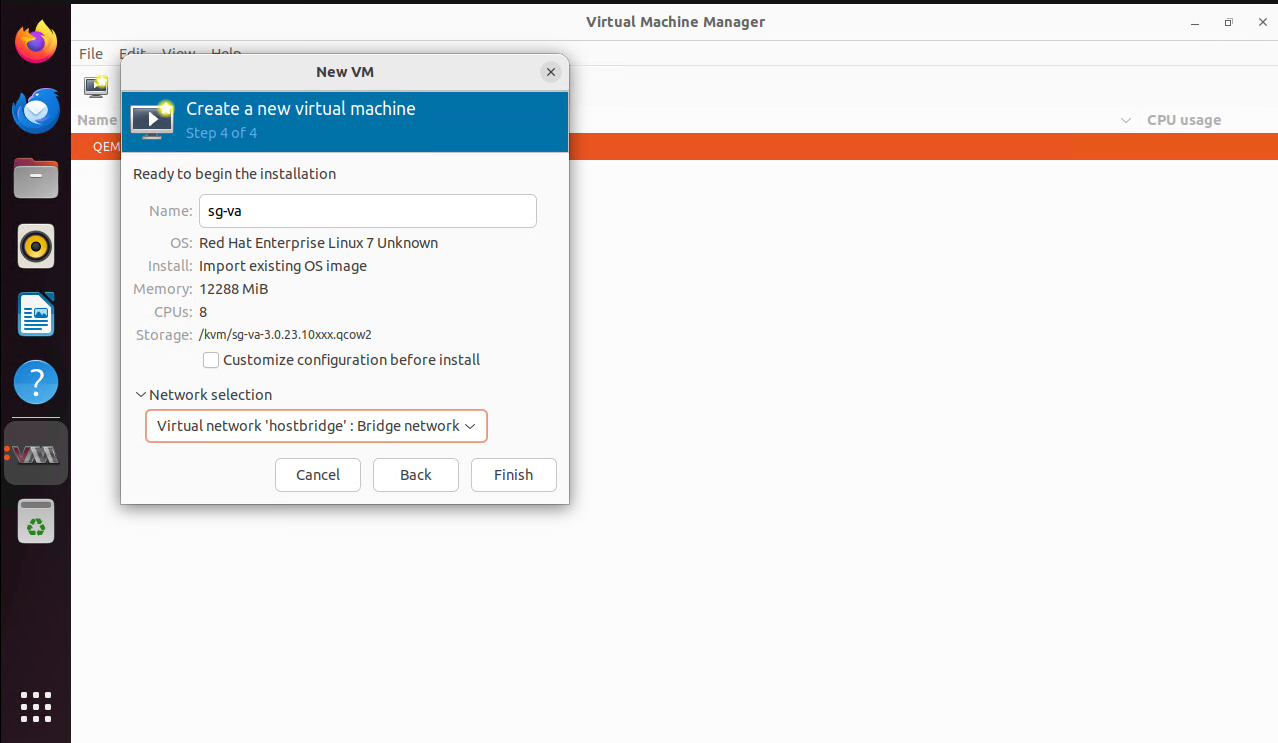
-
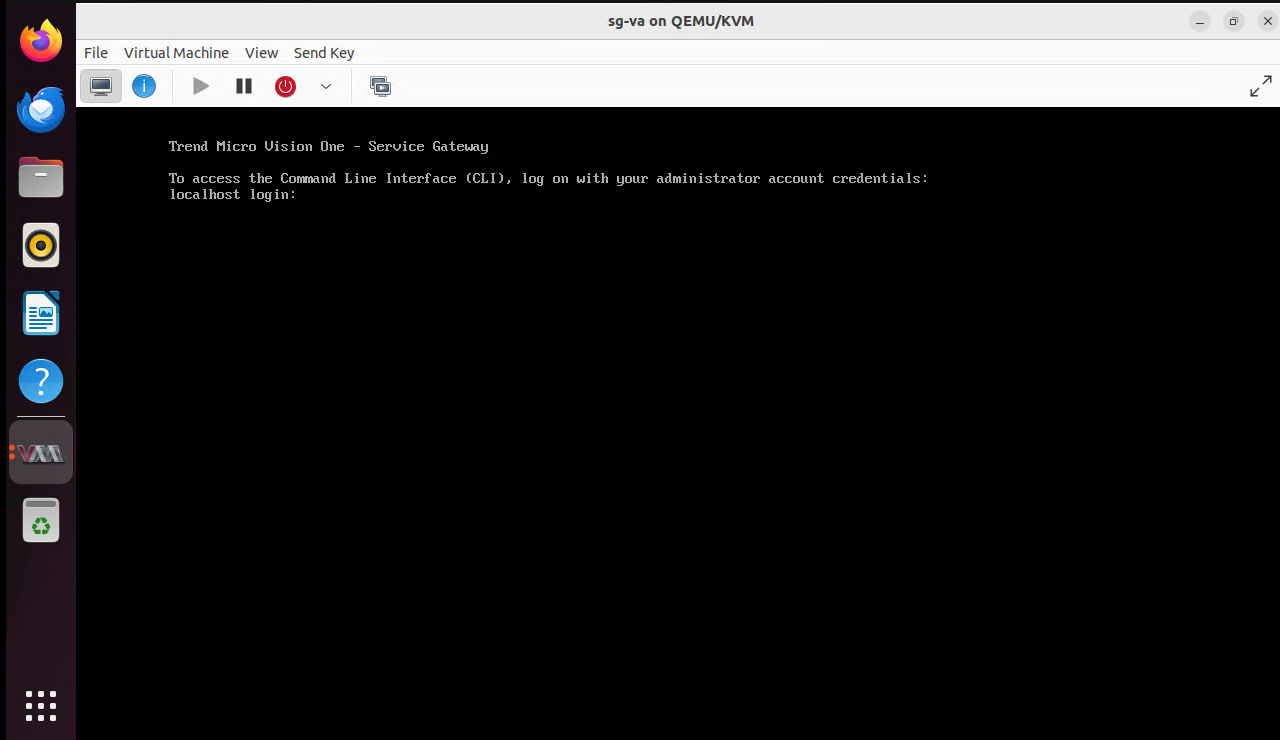
Start the VM.
-
-
- On the Service Gateway virtual appliance, log on to the Command Line Interface (CLI)
with the default credentials.User name: adminPassword: V1SG@2021
- Change your password.
- Type enable and press the
ENTERkey to enable administrative commands. Provide your password when asked.The command prompt changes from > to #. - Configure the required network settings using the following CLISH commands.
Configure network primary ipv4.static <interface> <ip_cidr> <gateway> <dns1> [dns2] [cni]Configure static IPv4 network settings for the primary network interface<interface>: Name of the network interface (for example, eth0)<ip_cidr>: IPv4 address of the network interface in CIDR notation<gateway>: Gateway router address<dns1>: Primary DNS server address[dns2]: Secondary DNS server address[cni]: Internal network address pool (IP address ending in .0.0) - To register the Service Gateway virtual appliance to TrendAI Vision One™, use an SSH tool, such as the latest version of PuTTY, and using an account with
administrator privileges, type the following command.
register <registration_token>You can obtain the token from the same screen you download the virtual appliance on TrendAI Vision One™ (step 4).
Important
The virtual appliance only supports UTC time. Ensure your hypervisor is correctly configured.
Note
-
If your environment uses a local Network Time Protocol (NTP) server, make sure the NTP server synchronizes with the local time for successful registration.
-
TrendAI™ recommends using an SSH client to easily copy and paste the registration token.
-
- Use the CLI to configure other settings, if required.For more information on available commands, see Service Gateway CLI commands.For details on setting up a virtual appliance with two network cards, see Service Gateway Virtual Appliance dual network card configuration.


