SAML is supported for sign-on and access to the Workload Security service and not
to the overall Trend Cloud One product.
SAML is supported for the following regions:
-
US:
https://app.deepsecurity.trendmicro.com -
India:
https://workload.in-1.cloudone.trendmicro.com -
UK:
https://workload.gb-1.cloudone.trendmicro.com -
Japan:
https://workload.jp-1.cloudone.trendmicro.com -
Germany:
https://workload.de-1.cloudone.trendmicro.com -
Australia:
https://workload.au-1.cloudone.trendmicro.com -
Canada:
https://workload.ca-1.cloudone.trendmicro.com -
Singapore:
https://workload.sg-1.cloudone.trendmicro.com
For information on how to implement SAML single sign-on, see Configure SAML single sign-on or Configure SAML single sign-on with Microsoft Entra ID.
SAML and single sign-on
Security Assertion Markup Language (or SAML) is an open authentication standard that
allows for the secure exchange of user identity information from one party to another.
SAML supports single sign-on, a technology that allows for a single user login to
work across multiple applications and services. For Workload Security, implementing
SAML single sign-on means that users signing in to your organization's portal would
be able to seamlessly sign in to Workload Security without an existing Workload Security
account.
SAML single sign-on in Workload Security
Sections below detail how SAML single sign-on works in Workload Security.
Establish a trust relationship
In SAML single sign-on, a trust relationship is established between two parties: the
identity provider and the service provider. The identity provider has the user identity
information stored on a directory server. The service provider (which in this case
is Workload Security) uses the identity provider's user identities for its own authentication
and account creation.
The identity provider and the service provider establish trust by exchanging a SAML
metadata document with one another.
At this time, Workload Security supports only the HTTP POST binding of the SAML 2.0
identity provider (IdP)-initiated login flow, and not the service provider (SP)-initiated
login flow.
Create Workload Security accounts from user identities
Once Workload Security and the identity provider have exchanged SAML metadata documents
and established a trust relationship, Workload Security can access the user identities
on the identity provider's directory server. However, before Workload Security can
actually create accounts from the user identities, account types need to be defined
and instructions for transforming the data format need to be put in place. This is
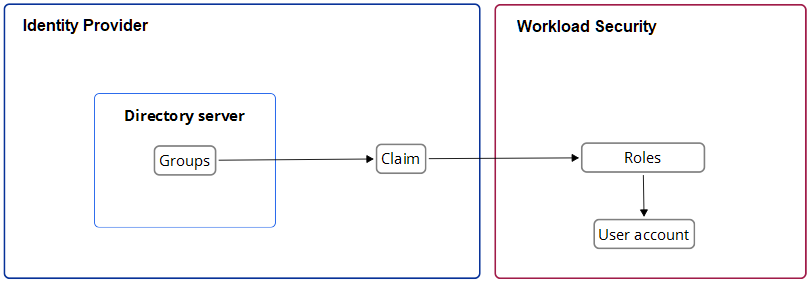
done using groups, roles, and claims.
Groups and roles specify the tenant and access permissions that a Workload Security
user account has. Groups are created on the identity provider's directory server.
The identity provider assigns user identities to one or more of the groups. Roles
are created in the Workload Security console. There must be both a group and a role
for each Workload Security account type, and their access permissions and tenant assignment
must match.
Once there are matching groups and roles for each user type, the group data format
needs to be transformed into a format Workload Security can understand. This is done
by the identity provider with a claim. The claim contains instructions for transforming
the group data format into the matching Workload Security role.
See SAML claims structure required by Workload Security.
The following diagram represents this process:
Implement SAML single sign-on in Workload Security
Once trust has been established between Workload Security and an identity provider
with a SAML metadata document exchange, matching groups and roles have been created,
and a claim put in place to translate the group data into roles, Workload Security
can use SAML single sign-on to automatically make Workload Security accounts for users
signing in through your organization's portal.
For more information on implementing SAML single sign-on, see Configure SAML single sign-on.


