Hosted Email Security will first scan incoming email messages before final delivery to the "example.com" Inbound Server.
The flow of messaging traffic from the Internet, through the Hosted Email Security, and then to the "example.com" Inbound Server, or local MTA.
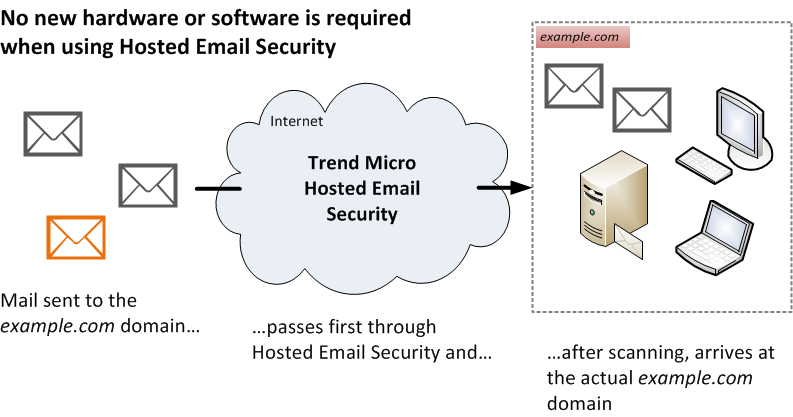
Evaluation is done in the following order:
-
The originating MTA performs a Domain Name Service (DNS) lookup of the MX record for "example.com" to determine the location of the "example.com" domain.
The MX record for "example.com" points to the IP address of the Hosted Email Security instead of the original "example.com" Inbound Server.
-
The originating MTA routes messages to Hosted Email Security.
-
The Hosted Email Security accepts the connection from the originating mail server.
-
Hosted Email Security performs connection-based filtering at the MTA connection level to decide on an action to take. Actions include the following:
-
Hosted Email Security terminates the connection, rejecting the messages.
-
Hosted Email Security accepts the messages and filters them using content-based policy filtering.
-
-
Hosted Email Security examines the message contents to determine whether the message contains malware such as a virus, or if it is spam, and so on.
-
Assuming that a message is slated for delivery according to the domain policy rules, the Hosted Email Security routes the message to the original "example.com" Inbound Server.


