NoteYou can enable Application Control for computers running version 10.0+ of the
agent. For a list of operating systems where Application Control is supported,
see Supported features by platform.
|
Application Control continuously monitors your protected servers for software changes
and allows or blocks them based on its enforcement setting, along with its computer
and policy configurations for software rulesets, global rulesets, and trust
entities:
- Application Control's enforcement setting (in a policy or computer's Application Control tab) can be set to either "block unrecognized software until it is explicitly allowed" or "allow unrecognized software until it is explicitly blocked". Which option you choose depends on the level of control you want over your environment.
- Rules in software rulesets either allow software to run or block it. Once a software change has been explicitly allowed or blocked from the Server & Workload Protection Actions page or from an Application Control event (in ), it is updated in the assigned software ruleset.
- Using the API, global rules allow you to enforce and track block rules that can be applied across all of your protected computers.
- The trust entities feature lets you configure trust rules to auto-authorize specific software changes based on predefined properties, avoiding entries that would otherwise appear and need to be manually allowed or blocked from the Actions page or Application Control Security Events page () in Server & Workload Protection.
To determine whether software is new or has changed, the agent compares a file's
SHA-256 hash and file size with its initially installed SHA-256 hash and file
size.
TipYou can automate Application Control creation and configuration
using the API. For more information, see Configure Application Control.
|
Key software ruleset concepts
The key software ruleset concepts are described below.
NoteFor information on how to auto-authorize software changes to reduce the
number that you manually allow or block using software rulesets, see
[Application Control Trust Entities]
|
Targeted protection state: One of the main decisions you need to
make when setting up Application Control is deciding your targeted protection
state. Do you want to prevent all new or changed software from running, unless
you manually specify that it is allowed? Or do you want it to run by default
unless you specifically block it? One approach is to initially allow
unrecognized software to run when you first enable Application Control and
there's a lot of unrecognized software. As you add Application Control rules and
the volume of unrecognized software decreases, you could switch to block
mode.
Software ruleset rules: Rules specify whether software is allowed or
blocked on a particular computer.
Inventory: Initial list of software that is installed on the
computer. Make sure only software that you want to allow is installed on the
computer. When you enable Application Control, all currently installed software
is added to the computer's inventory and allowed to run. When a computer is in
maintenance mode, any software changes made to the computer are added to the
computer's inventory and allowed to run. A computer's software inventory list is
stored on the agent and is not displayed in the Server & Workload Protection console.
Unrecognized software: Software that isn't in a computer's inventory
and isn't already covered by an Application Control rule. See What does Application Control detect as a
software change?
Maintenance mode: If you are planning to install or update software,
we strongly advise that you turn on maintenance mode. In maintenance mode,
Application Control continues to block software that is specifically blocked by
an Application Control rule, but allows new or updated software to run and adds
it to the computer's inventory list. See Turn on maintenance mode when making planned changes.
How do Application Control software rulesets work?
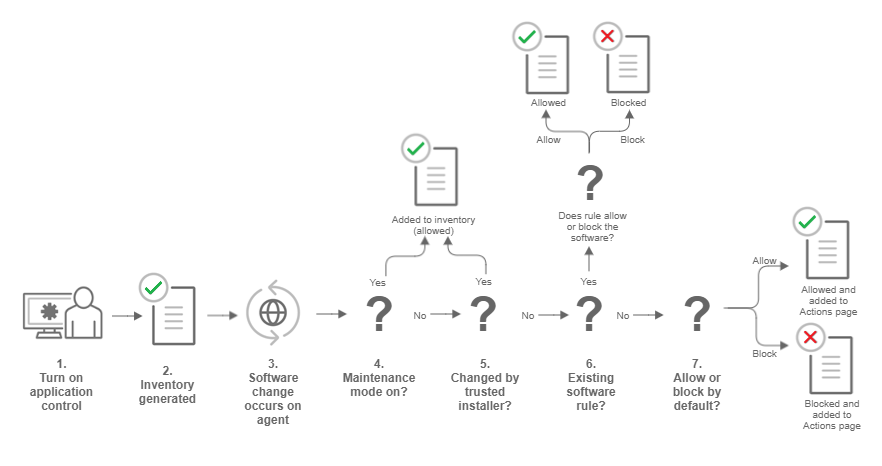
Procedure
- You enable Application Control in a policy and assign the policy to a
computer that is protected by an agent (see Turn on Application Control).
- When the agent receives the policy, it creates an inventory of all software installed on the computer. All software listed in the inventory is assumed to be safe and is allowed to run on that computer. This inventory list is not visible from the Server & Workload Protection console, which means you need to be absolutely certain that only good software is installed on a computer where you intend to enable Application Control.
- After the inventory is finished, Application Control is aware of any
software changes on the computer. A software change could be new software
that appears on the computer or changes to existing software.
- If the computer is in maintenance mode, the agent adds the software to its inventory and it is allowed to run. This change is not visible in the Server & Workload Protection console. See Turn on maintenance mode when making planned changes.
- If the change was made by a trusted installer, the agent adds the software
to its inventory and allows it to run. For example, when Microsoft Windows
self-initiates a component update, hundreds of new executable files may be
installed. Application Control auto-authorizes many file changes that are
created by well-known Windows processes and does not list these changes in
the Server & Workload Protection console. Removing the
"noise" associated with expected software changes provides you
with clearer visibility into changes that may need your attention.

Note
The trusted installer feature is available with agent version 10.2 or later. - If the computer's software ruleset contains a rule for this exact piece of
software, the software is allowed or blocked according to the rule that's in
place. See What does Application
Control detect as a software change?
- If software is not in the computer's inventory and is not covered by an
existing rule, it's considered unrecognized software. The policy assigned to
the computer specifies how unrecognized software is handled. Depending on
the policy configuration, it's either allowed to run or is blocked. If the
software is blocked and it is able to produce error messages in the OS, an
error message on the protected computer indicates that the software does not
have permissions to run or that access is denied.The unrecognized software appears on the Application Control - Software Changes page in the Server & Workload Protection console. On that page, an administrator can click Allow or Block to create an allow or block rule for that piece of software on a particular computer. An allow or block rule takes precedence over the default action specified in the policy. See Monitor new and changed software.
A tour of the Application Control interface
There are a few places in the Server & Workload Protection
console where you can see changes related to Application Control:
Application Control: Software Changes (Actions)
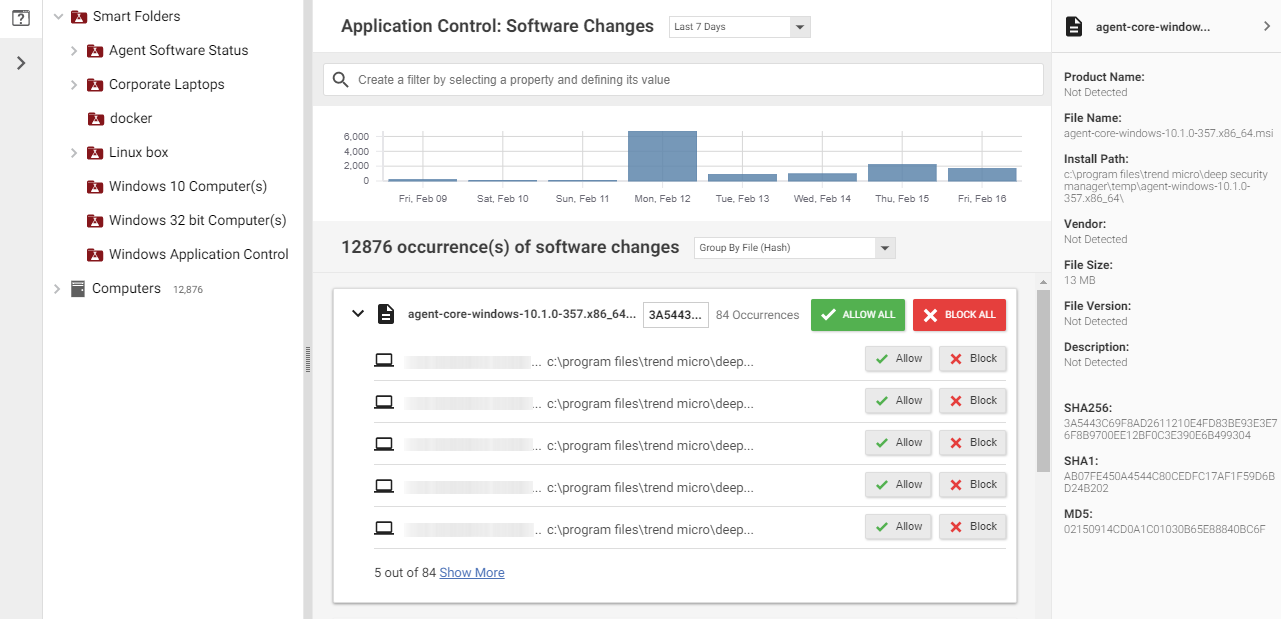
The Application Control: Software Changes page is displayed when you
click Actions in the Server & Workload Protection
console. It displays all unrecognized software (software that isn't in a
computer's inventory and doesn't have a corresponding Application Control rule).
Software changes are allowed or blocked at the computer level, so if a
particular piece of software is installed on fifty computers, it will appear on
that page fifty times. However, if you know that a certain piece of software
should be allowed or blocked everywhere, you can filter the Actions
page to sort the changes by file hash and then click Allow All to
allow it on all computers where the software is installed.
The policy applied to a computer specifies whether it will allow all unrecognized
software to run by default, or block all unrecognized software, but no explicit
Application Control rule is created until you click "Allow" or
"Block" on the Actions page. When you click Allow or
Block, a corresponding rule appears in the software ruleset for the computer
(under ).
Application Control Software Rulesets
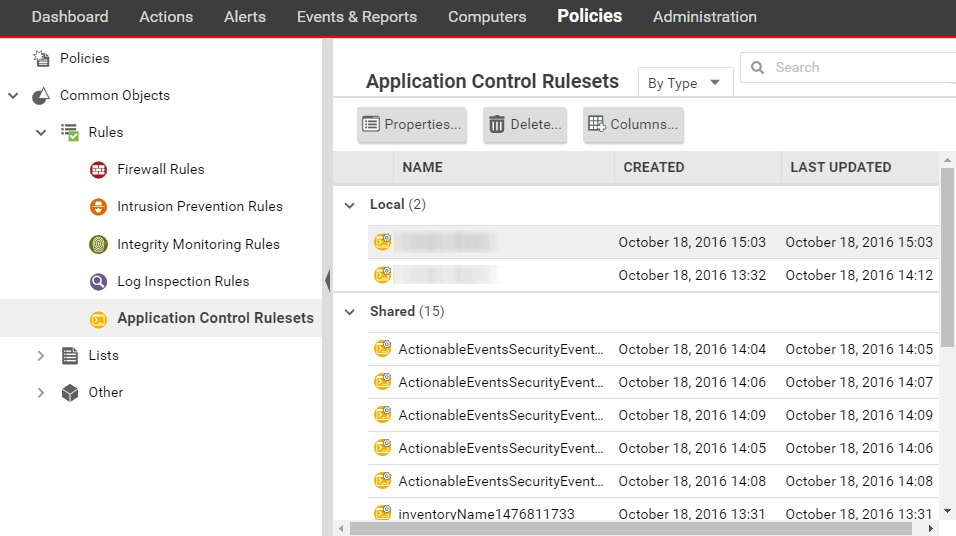
To see the software ruleset for a computer, go to . To see which rules are part of a ruleset, double-click the
ruleset and go to the Rules tab. The Rules tab displays the pieces
of software that have rules associated with them and enables you to change allow
rules to block, and vice versa.
Security Events
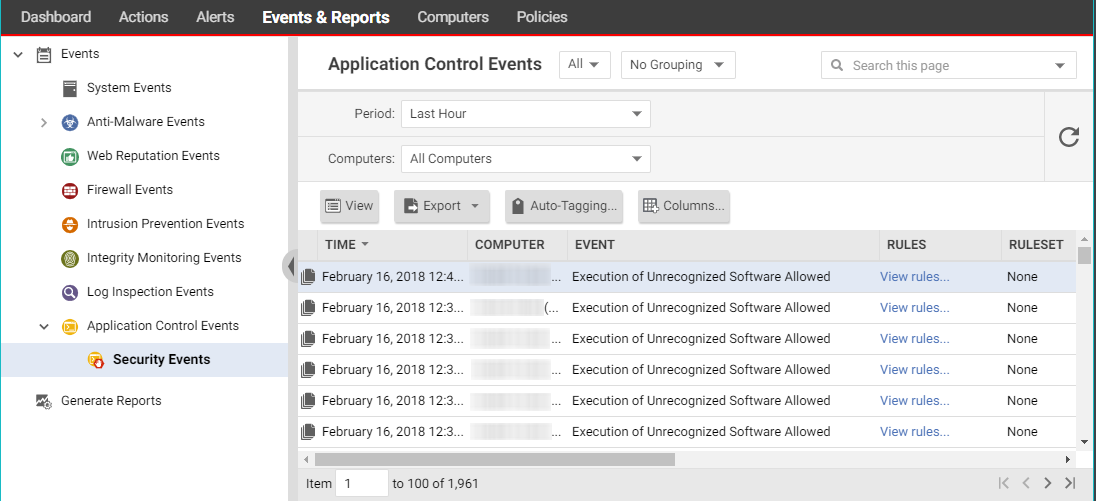
displays all unrecognized software that either has been run on a
computer or has been prevented from running by a block rule. You can filter this
list by time period and other criteria.
For each event (except aggregated events), you can click View rules
to change the rule from Allow to Block or vice versa. The version 10.2+ agent
includes event aggregation logic to reduce the volume of logs when the same
event occurs repeatedly.
Application Control Trust Entities
shows trust rulesets and trust rules which you can configure to
auto-authorize software changes. For more information, see Application Control trust entities.
What does Application Control detect as a software change?
Unlike integrity monitoring, which monitors any file, Application Control
looks only for software files when examining the initial installation and
monitoring for change.
Software can be:
- Windows applications (.exe, .com, .dll, .sys), Linux libraries (.so) and other compiled binaries and libraries
- Java .jar and .class files, and other compiled byte code
- PHP, Python, and shell scripts, and other web apps and scripts that are interpreted or compiled on the fly
- Windows PowerShell scripts, batch files (.bat), and other Windows-specific scripts (.wsf, .vbs, .js)
For example, WordPress and its plug-ins, Apache, IIS, nginx, Adobe Acrobat,
app.war, and /usr/bin/ssh would all be detected as software.
Application Control checks a file's extension to determine whether it's a script.
Additionally, on Linux, Application Control treats any file with execute
permissions as if it's a script.
NoteOn Windows computers, Application Control tracks changes on the local file
system, but not on network locations, CD or DVD drives, or USB devices.
|
Application Control is integrated with the kernel (on Linux computers) and file
system, so it has permissions to monitor the whole computer, including software
installed by root or administrator accounts. The agent watches for disk write
activity on software files, and for attempts to execute software.


