This widget displays the total number of unique critical threat types detected on your network and the number of affected users and threat detections for each threat type.
Click the settings icon () to change the default View.
-
On the Summary tab or a custom tab, the Affected users view is selected by default.
-
On the Threat Investigation tab, the Threat detections view is selected by default.
-
The widget lists critical threat types in order of severity.
-
Individual users may be affected by more than one critical threat type.
Use the Range drop-down to select the time period for the data that displays.
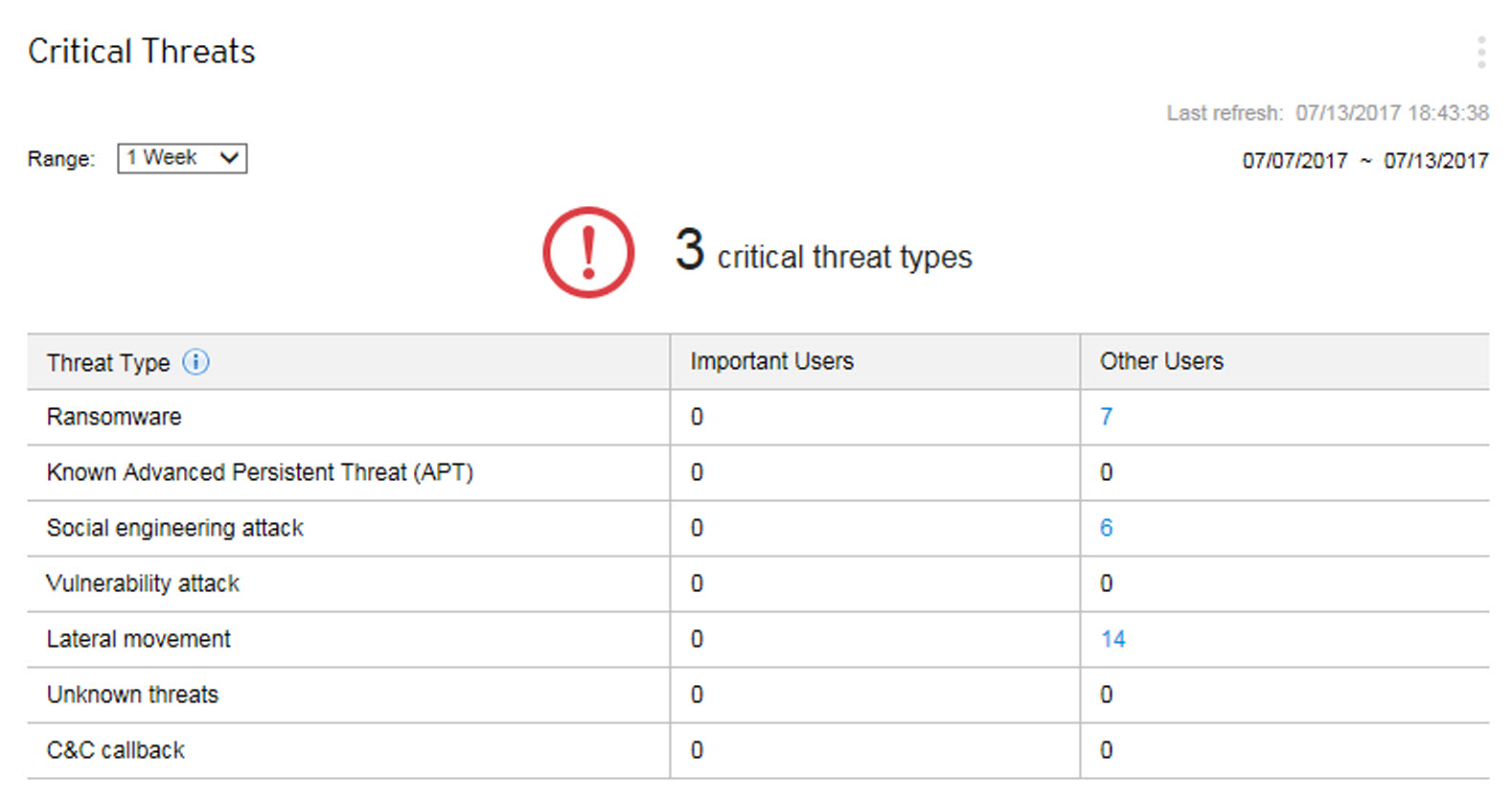
The Affected users view displays the number of Important Users and Other Users affected by each threat type.
-
Click the count in the Important Users or Other Users column, and then click the affected user you want to view.
-
You can define important users or endpoints on the User/Endpoint Directory screen.
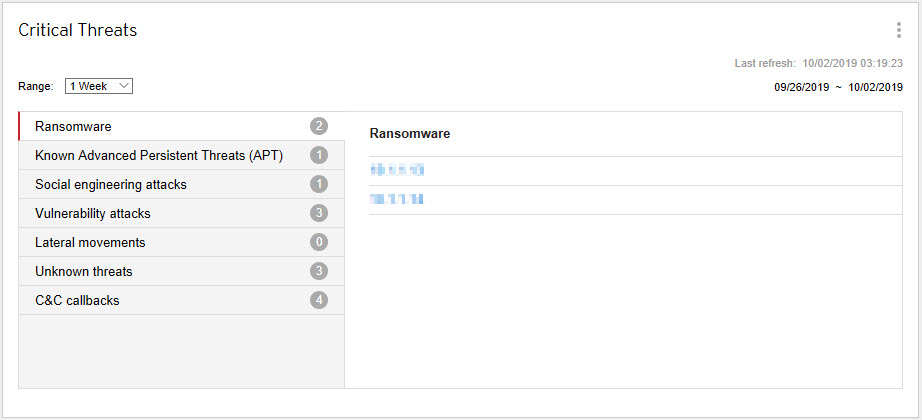
The Threat detections view displays the number of detections for each critical threat type.
-
Click a critical threat type to view the specific threat detections.
-
Click the hyperlink for a specific threat detection to view details about the affected users and automatically start a Root Cause Analysis to determine whether the threat has affected other endpoints on your network.
Critical threat detections include the following threat types.
|
Threat Type |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Ransomware |
Malware that prevents or limits users from accessing their system unless a ransom is paid |
|
Known Advanced Persistent Threats (APT) |
Intrusions by attackers that aggressively pursue and compromise chosen targets, often conducted in campaigns—a series of failed and successful attempts over time to get deeper and deeper into a target network—and not isolated incidents |
|
Social engineering attacks |
Malware or hacker attacks that exploits a security vulnerability found in documents, such as a PDF file |
|
Vulnerability attacks |
Malware or hacker attacks that exploits a security weakness typically found in programs and operating systems |
|
Lateral movements |
Searches for directories, email, and administration servers, and other assets to map the internal structure of a network, obtain credentials to access these systems, and allow the attacker to move from system to system |
|
Unknown threats |
Suspicious objects (IP addresses, domains, file SHA-1 hash values, email messages) with the "high" risk level, as detected by Deep Discovery Inspector, endpoint security products, or other products with Virtual Analyzer |
|
C&C callbacks |
Attempts to communicate with a command-and-control (C&C) server to deliver information, receive instructions, and download other malware |


