Visualize how the Virtual Network Sensor fits into your network environment before planning your deployment.
The following maps provide an overview of deployment scenarios tested and supported
by the
Virtual Network Sensor. Use these maps to help guide your deployment plans to best
meet the
needs of your network. Each scenario contains a link to the post-deployment network
configuration steps for the mapped configuration.
-
To monitor network traffic within the host machine the Virtual Network Sensor is deployed on, see Internal network traffic scenario.
-
To monitor network traffic between virtual machines deployed on a different host machine than the Virtual Network Sensor, see External inter-VM traffic scenario.
-
To monitor all network traffic passing through a physical network switch, see External traffic scenario.
-
For monitoring traffic bandwidth above 2 Gbps regardless of source, see External traffic PCI passthrough scenario.
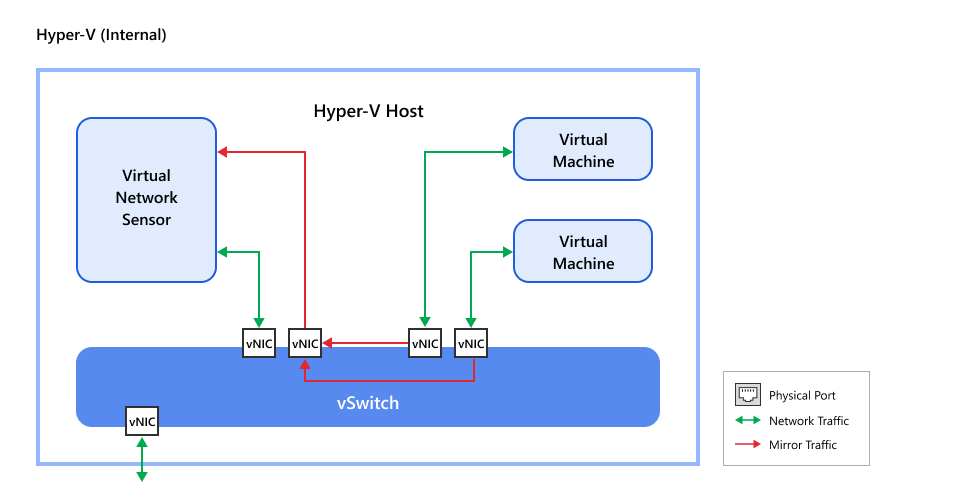
Internal network traffic scenario
Internal network traffic refers to traffic occurring within the host machine where
the
Virtual Network Sensor is deployed. This scenarios is best for monitoring traffic
between
virtual machines on the same Hyper-V host as the Virtual Network Sensor. Traffic is
mirrored
from a virtual network switch set up on the host machine to the Virtual Network Sensor
data
port virtual NIC.
Review the scenario below to determine if it is the best fit for your network.
-
Internal network traffic on Hyper-V hostTo configure your network using this scenario, see Configure internal network traffic on Hyper-V host.
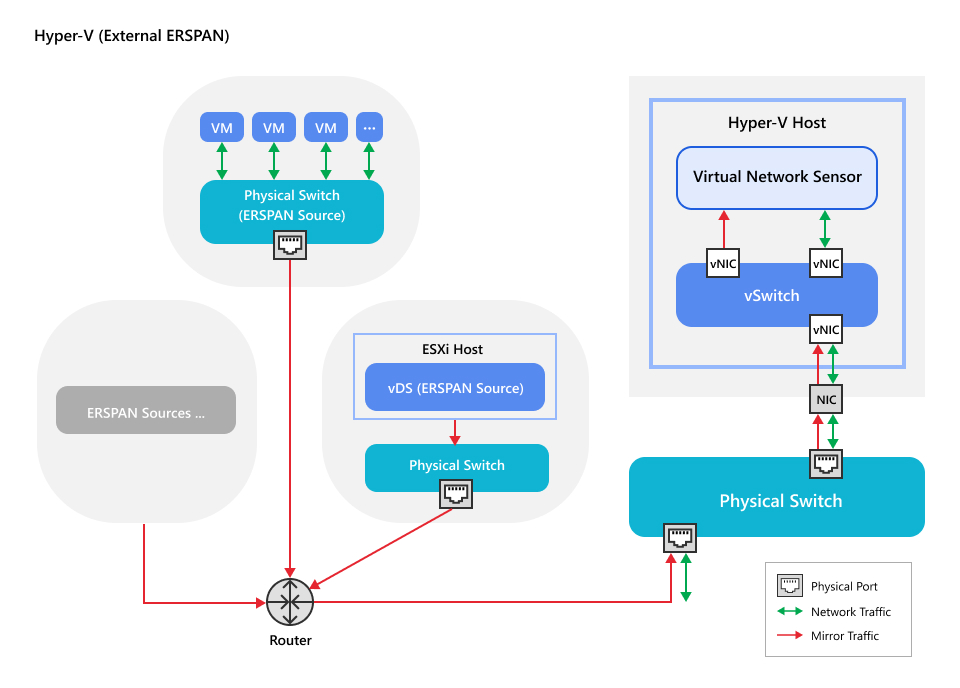
External inter-VM traffic scenario
External traffic refers to any scenario where monitored traffic is mirrored from a
source
outside of the host machine where the Virtual Network Sensor is deployed. External
inter-VM
deployments are best for monitoring traffic between virtual machines on a different
host
form the Virtual Network Sensor. Traffic is mirrored from a virtual network switch
set up on
the source host machine, through a physical network switch, to the Virtual Network
Sensor
via the physical network connection of the host Hyper-V machine.
Virtual Network Sensor has been tested and supports the external inter-VM scenario
using
ERSPAN. Review the scenario below to determine if it is the best fit for your network.
-
External inter-VM network traffic (ERSPAN)To configure your network using this scenario, see Configure external inter-VM traffic with ERSPAN (Hyper-V host).
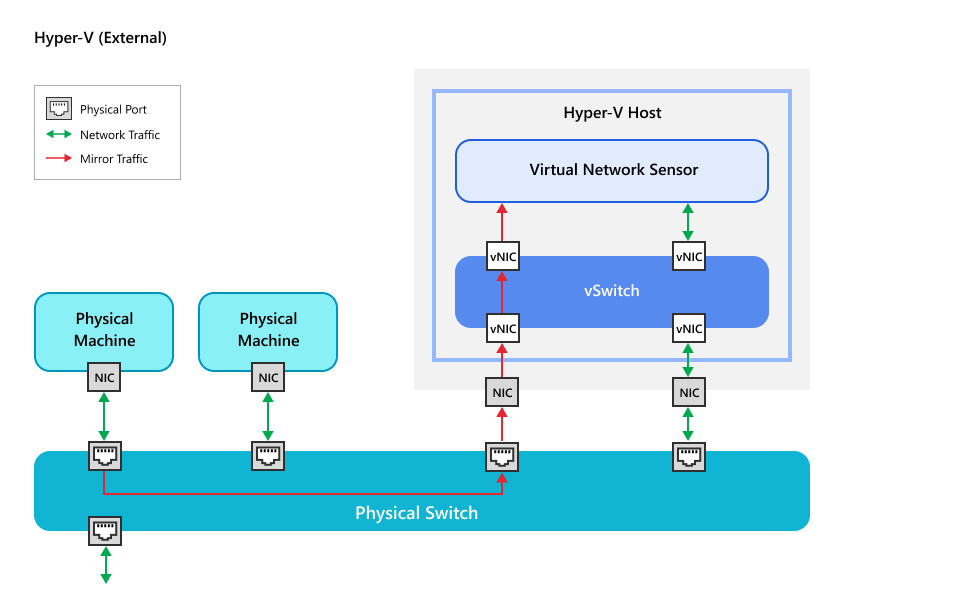
External traffic scenario
External traffic refers to any scenario where monitored traffic is mirrored from a
source
outside of the host machine where the Virtual Network Sensor is deployed. This scenario
is
best for monitoring traffic on your network as it passes through a physical network
switch.
Traffic is mirrored from source physical network switch to the Virtual Network Sensor
via
the physical network connection of the host Hyper-V machine.
Review the scenario below to determine if it is the best fit for your network.
-
External network trafficTo configure your network using this scenario, see Configure external network traffic on Hyper-V host.
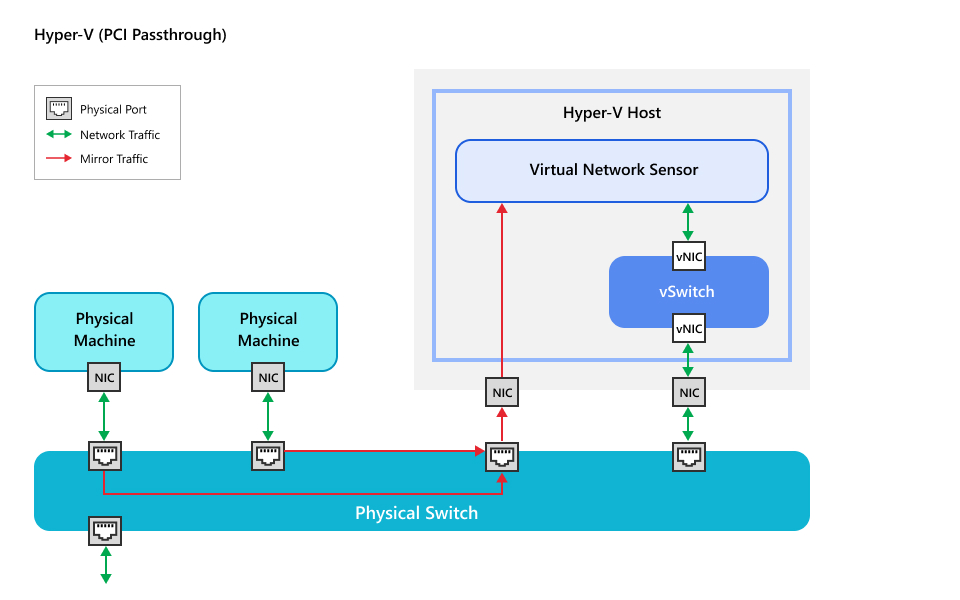
External traffic PCI passthrough scenario
External traffic refers to any scenario where monitored traffic is mirrored from a
source
outside of the host machine where the Virtual Network Sensor is deployed. This scenario
is
best for deploying a Virtual Network Sensor with an expected bandwidth throughput
greater
than 2 Gbps. Traffic is mirrored from a source physical network switch to the Virtual
Network Sensor via a physical connection configured for PCI passthrough on the host
machine.
Review the scenario below to determine if it is the best fit for your network.
-
PCI passthroughTo configure your network using this scenario, see Configure external network traffic with PCI passthrough (Hyper-V host).