|
|
|
TipTrend Micro recommends using the same device size
for each device in a RAID array. In a Microsoft Windows environment, the maximum volume
size is 2TB
for simple and mirrored volumes and up to 64TB for Windows striped volumes (2TB per
disk with a
maximum of 32 disks per volume).
In Amazon EC2, Trend Micro recommends limiting the
RAID array to a maximum of eight devices. In a CSP environment, the maximum number
of devices you
can add to a RAID array is 32.
|
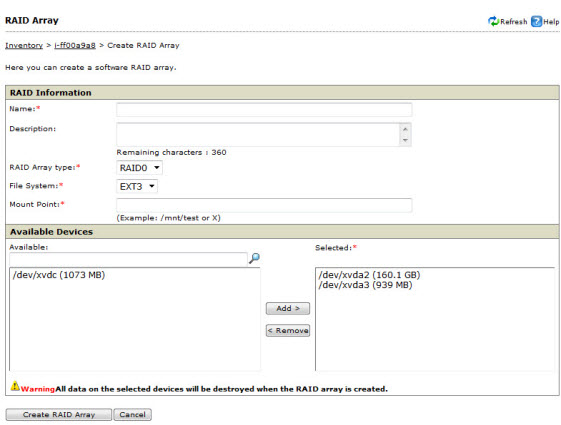
WARNINGAll data on the selected devices is erased when the RAID array is created.
|